HDMR – Heated Dot Magnetic Recording is based on ultra small, non-interacting, and thermally stable (at room temperature) magnetic dots. They are heated by laser, as with HAMR, to lower their resistance to magnetic polarity changes (coercivity) and so enable bit value writing.
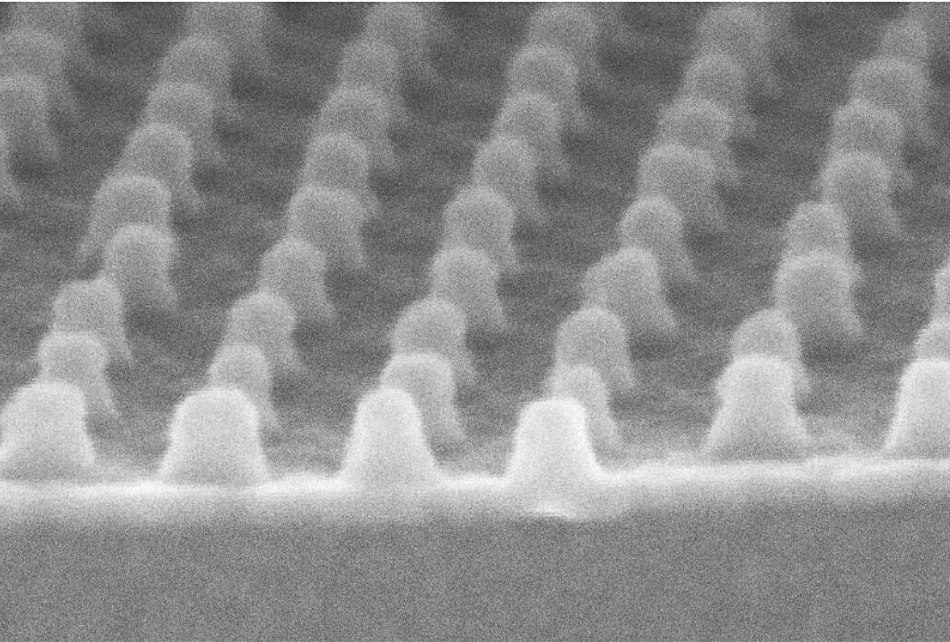
HDMR can be viewed as a combination of HAMR and bit-patterned media (BPM) with one isolated island used per bit. With BPM there is an array of lithographically defined magnetic islands as opposed to PMR and HAMR which have a recording medium composed of a dense collection of random grains about 10nm in diameter. A recording bit is an area, hundreds of nanometers in size, a magnetic domain, containing many such grains, each of which have the same magnetic polarity.







